编写Beep函数的POC代码和frida脚本(模拟检测沙箱),模拟Beep规避沙箱的检测机制。
Beep函数#
Beep函数在微软文档中描述为“在扬声器上生成简单的音调。该函数是同步的;它执行一个可警报的等待,直到声音结束后才将控制权返回给调用者。”
“Generates simple tones on the speaker. The function is synchronous; it performs an alertable wait and does not return control to its caller until the sound finishes.”
BOOL Beep(
[in] DWORD dwFreq,
[in] DWORD dwDuration
);
上述文档描述了,Beep函数在播放音调时的行为特性——即同步执行和可警报等待机制,并强调了它在播放完声音之前不会返回控制权给调用者。
而一些沙箱环境可能不会完全模拟这种硬件交互和等待机制,某些恶意软件将这种特性滥用,把beep函数用于反沙箱检测,。比如,哈希值为ab5dc89a301b5296b29da8dc088b68d72d8b414767faf15bc45f4969c6e0874e的Beep malware样本采用十余种规避技术,其中一种就利用了这种特性。(该样本的分析可见https://www.swascan.com/beep-analisi-malware/)
这是一个有趣的反沙箱和反调试技术,接下来将通过POC代码模拟Beep的规避行为,更深入了解Beep函数。
POC与Hook检测#
设计的基本实验思路如下图:
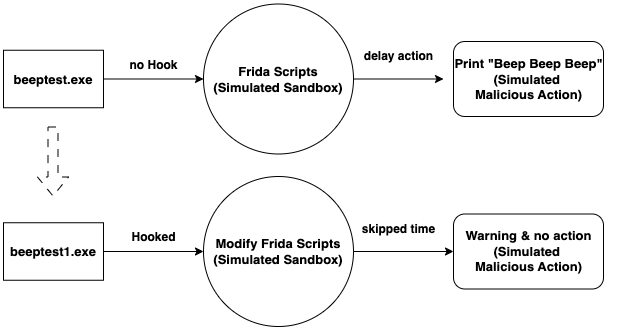
先将初始的Beep 函数的POC代码beeptest.exe用无修改参数的Frida脚本beep.py模拟沙箱检测,按照设定的延迟时间进行正常执行,输出Beep Beep Beep!字符串。然后将beeptest.exe更改为beeptest1.exe,添加真实时间执行的异常校验逻辑;对应地,将Frida脚本beep.py进行修改为beep_modified.py,添加延迟时间修改的功能,模拟沙箱检测。此时,beeptest1.exe被Hook后告警Running in a sandbox environment!、不输出Beep Beep Beep!字符串。
详细步骤和效果如下所述。
编写POC代码beep.go,通过Beep实现延迟执行的效果,代码如下:
//模拟beep的延迟执行
package main
import (
"fmt"
"syscall"
"time"
)
var (
// Import kernel32.dll
kernel32 = syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll")
// Import Beep function
procBeep = kernel32.NewProc("Beep")
)
func main() {
start := time.Now()
// Call Beep function with frequency 750Hz and duration 60ms
procBeep.Call(750, 60)
fmt.Println("[+] Set Duration: ", 60*time.Millisecond)
duration := time.Since(start)
fmt.Println("[+] Actual Duration: ", duration)
fmt.Println("[+] Beep Beep Beep!")
}
为了减少实验等待时间、增加实验的效果,并未将Beep的时长调的过长。而现实的恶意软件时长有调至很长的,如65000毫秒,导致分析停滞约1分钟。
因为沙箱负载了数很多样本,大多沙箱追求的是检测高效性,需要在短时间内完成对样本的自动化检测,沙箱模拟通常持续很短的时间,仿真时间很少超过3~5分。
编写Python脚本beep.py,利用frida的Hook模拟沙箱,初始版本无延迟检测和操纵时间功能:
#利用frida模拟沙箱的初级安全检测,无延迟检测和操纵时间功能
import sys
import frida
def main(target_process):
# Spawn the target process and attach to it
pid = frida.spawn(target_process)
session = frida.attach(pid)
# Define the Frida script to hook Beep function
script = session.create_script("""
console.log("|__> Starting Frida script");
// Resolve the address of the Beep function in kernel32.dll
var beepAddr = Module.findExportByName("kernel32.dll", "Beep");
console.log("|__> Hooking Beep at " + beepAddr);
Interceptor.attach(beepAddr, {
onEnter: function(args) {
console.log("|__> Called Beep");
console.log("|__> Frequency: " + args[0].toInt32());
console.log("|__> Duration: " + args[1].toInt32());
},
onLeave: function(retval) {
console.log("|__>|__> Returned from Beep");
}
});
""")
# Load the script into the target process
script.load()
# Resume the target process
frida.resume(pid)
# Keep the script running
sys.stdin.read()
# Detach when done
session.detach()
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: %s <target_program>" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
main(sys.argv[1])
Python脚本 beep.py 对beeptest.exe的频率、时长无检测,beeptest.exe 通过Beep()函数可实现延迟攻击,在蜂鸣时间到达之后输出Beep Beep Beep!字符串。此处模拟,沙箱在仿真时间完成后,beeptest.exe还在休眠未执行真实意图代码,从而绕过沙箱的检测:

为了解决这种问题,有的沙箱可以实现操纵时间和执行延迟的功能。例如,Cuckoo 沙箱具有休眠跳过功能,可以用非常短的值替换延迟,迫使恶意软件在分析超时之前开始其恶意活动。(见checkpoint的文章Evasions: Timing )
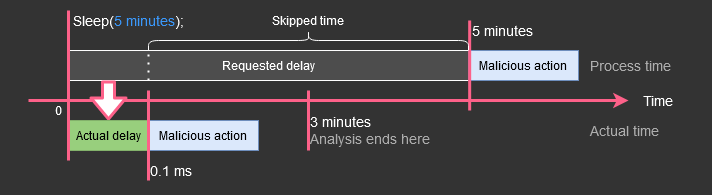
在本实验中,如果改进Python脚本 beep.py 为beep_modified.py,利用frida的Hook修改目标程序的“蜂鸣时间”(即,休眠时间),实现实验中“沙箱”的升级。
frida脚本beep_modified.py对beeptest.exe的频率、时长进行Hook,动态缩小频率和时长,加快执行beeptest.exe 的程序流:
import sys
import frida
def main(target_process):
pid = frida.spawn(target_process)
session = frida.attach(pid)
script = session.create_script("""
console.log("|__> Starting Frida script");
var beepAddr = Module.findExportByName("kernel32.dll", "Beep");
console.log("|__> Hooking Beep at " + beepAddr);
Interceptor.attach(beepAddr, {
onEnter: function(args) {
console.log("|__> Called Beep");
console.log("|__> Original Frequency: " + args[0].toInt32());
console.log("|__> Original Duration: " + args[1].toInt32());
// 修改频率和时间参数
args[0] = ptr(2); // 设置频率为2Hz
args[1] = ptr(20); // 设置时间为20ms
console.log("|__> Modified Frequency: " + args[0].toInt32());
console.log("|__> Modified Duration: " + args[1].toInt32());
},
onLeave: function(retval) {
console.log("|__>|__> Returned from Beep");
}
});
""")
script.load()
frida.resume(pid)
sys.stdin.read()
session.detach()
if __name__ == '__main__':
if len(sys.argv) != 2:
print("Usage: %s <target_program>" % sys.argv[0])
sys.exit(1)
main(sys.argv[1])
修改频率和时间参数,将beeptest.exe程序原有的频率750HZ设置为2HZ、时间60ms设置为20ms,加速程序的执行,顺利打印出Beep Beep Beep!字符串:
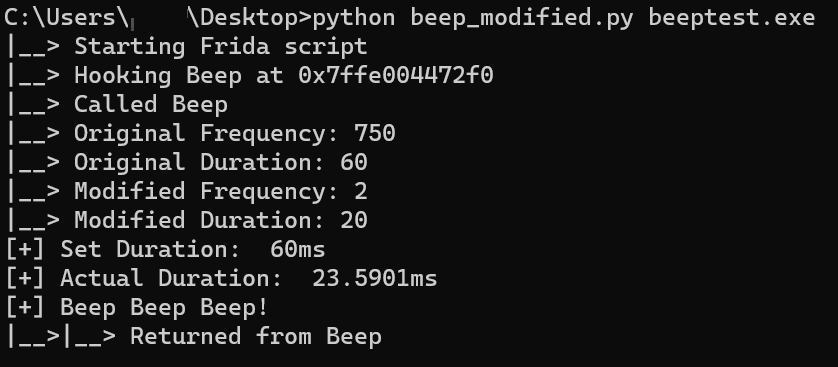
伴随着实验“沙箱”的升级——用非常短的值替换延迟,而这种休眠跳过技术也可以被绕过。 以下的方法可见Evasions: Timing
- 使用多种不同方法并行延迟
- 使用多种方法测量真实执行时间
- 使用多种方法获取系统时间
- 检测调用延迟函数后延迟值是否变化
- 从另外的进程获取时间,做差异化比较
- 从NTP、HTTP等外部源获取当前日期和时间
- 使用RDTSC测量虚拟环境和主机系统的时间差异
- 检测系统上次关闭、启动时间,做差异化比较
- 使用无效参数调用可能被Hook的延迟函数
在本实验中,将设定时间与测量真实执行时间做差异化比较的逻辑,从而实现绕过检测/探测仿真环境。将beeptest.exe 的源码beep.go代码更改为beep1.go代码,增加对实际时长有效性的判断,一旦时长异常,将打印出沙箱探测的相关信息——[-] Running in a sandbox environment或[!] Not running in a sandbox environment!"。beep1.go代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"syscall"
"time"
)
var (
// Import kernel32.dll
kernel32 = syscall.NewLazyDLL("kernel32.dll")
// Import Beep function
procBeep = kernel32.NewProc("Beep")
)
func isSandbox() bool {
start := time.Now()
// Call Beep function with frequency 750Hz and duration 60ms
procBeep.Call(750, 60)
duration := time.Since(start)
fmt.Println("[+] Actual Duration: ", duration)
// Check the beep duration was unexpectedly short
if duration < 60*time.Millisecond {
fmt.Println("[+] Set Duration: ", 60*time.Millisecond)
return true
}
return false
}
func main() {
if isSandbox() {
fmt.Println("[-] Running in a sandbox environment!")
} else {
fmt.Println("[!] Not running in a sandbox environment!")
fmt.Println("[+] Beep Beep Beep!")
}
}
使用frida脚本模拟沙箱对Beep的检测,beep.py脚本不会更改beeptest1.exe (beep1.go代码编译的程序)的延迟时间,beeptest1.exe 正常执行,打印出[+] Beep Beep Beep!字符串。beep_modified.py更改beeptest1.exe 执行时间,beeptest1.exe 对此打印出检测到沙盒环境的[-] Running in a sandbox environment!字符串:
本文编写Beep函数的POC代码和frida脚本(模拟沙箱),简化地模拟基于时间延迟的沙箱规避技术,并简单地升级了彼此的攻防对抗。而这种攻防对抗在现实中仍在持续进行,从检测和防御的角度来看,如果单一地对这种延迟进行时间Hook与操纵,只会让这类攻击逃之夭夭。
本文实验相关代码已上传github,见https://github.com/Netero0o0/beep-antisandbox
This is a practical case for educational purposes only.


